


The Trails
Guide
Maps
Miles/Ele
Permits
Resupply
Forum
Current Weather Conditions
Weather Notes
Northern High Sierras
Central High Sierras
Southern High Sierras
Gear
Gear List
Gettin Started
Layering
Discussion
Testing yourself and your gear
Gear Reviews
Roughing It
Samuel Clemmen's Experiences
in the
High Sierra Nevada
1861 to 1867
Languages
Languages
Trail Arts
The art of walking
Physical Preperation
Trail Skills
The trail
Off the trail
Scrambling
Maps
Navigation
Camp skills
Food
Resupply
Food
Other
Photo Catagories
Trail Stories
Trail Culture
News and Science
Links
Groups
Books
Terms and Conditions of Use
Traill Guide |
Traill Guide INDEX Echo Summit to Carson Pass |
West Tahoe Basin Map Desolation Wilderness |
South Tahoe Basin Map Meiss Country |
Meeks Bay to Echo Summit Miles and Elevations |
Echo Summit to Carson Pass Miles and Elevations |
High Sierra History and Monuments FORUM |
High Sierra Weather | all |
Mark Twain's Sierra Nevada
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
This book is merely a personal narrative, and not a pretentious history or a philosophical dissertation. It is a record of several years of variegated vagabondizing, and its object is rather to help the resting reader while away an idle hour than afflict him with metaphysics, or goad him with science. Still, there is information in the volume; information concerning an interesting episode in the history of the Far West, about which no books have been written by persons who were on the ground in person, and saw the happenings of the time with their own eyes. I allude to the rise, growth and culmination of the silver-mining fever in Nevada—a curious episode, in some respects; the only one, of its peculiar kind, that has occurred in the land; and the only one, indeed, that is likely to occur in it. Yes, take it all around, there is quite a good deal of information in the book. I regret this very much; but really it could not be helped: information appears to stew out of me naturally, like the precious ottar of roses out of the otter. Sometimes it has seemed to me that I would give worlds if I could retain my facts; but it cannot be. The more I calk up the sources, and the tighter I get, the more I leak wisdom. Therefore, I can only claim indulgence at the hands of the reader, not justification. THE AUTHOR. |
| Index Twain's Physical and Cultural Descriptions of the Sierra Nevada |
|||||||||
|
Twain's Trip West and quick emersion into the Wild West by Stagecoach |
Lake Tahoe in 1861 |
|
Descriptions of Lake Tahoe |
Silver Boom Culture |
Southeastern Sierra Nevada |
||||
Introduction Twain's unique perspective and uncanny skill at uncovering and describing human motivation and emotion gives us an unparalleled view into the character of the Silver Boom that swept across the Sierra during the 1850s and 60s, in the wake of the Gold Rush. The link above is to a complete copy of the first edition of Roughing It, with illustrations. This is the first of what I hope will be a series of pages reviewing the literary history of the Sierra Nevada. I strongly suggest you read Roughing It, Mark Twain's amazing contemporary account of the "Wild West," as he saw it in beginning in 1861. Introduction But, as many of you have not, and will not read Twain's views of the early Western West, I have taken the liberty of extracting some of Twain's most interesting quotes, observations, lines, lies, and insights which may cheaply enhance your understanding of the history of the locations we are hiking through, without having to read Twain. The index above details Twain's early looks at some of our favorite places. As I complete this trail guide I will uncover more of the history underlaying the Sierra trails we're walking across on our hike from Lake Tahoe to Mount Whitney, and post them up in the history forum for our edification and enjoyment. Mine, anyway. Remember that old Tom Petty rock song, "I need to Know?" Yeah, that's what it feels like. In this case we need to know and feel the historical echoes of our footsteps. We need to know. There is a History section in the Forum, where you can add to or check out what we've put together so far. Share your resources and perspectives on the History of the Sierra Nevada Mountains. I need to know! Note: When you click the links to the Guttenberg Press' Roughing It, it may take a moment for your browser to access the whole file of the book. After that delay all the links load instantly. Comments and questions about Clemmens are welcome. I'm no expert, have no answers, and will likely lower your IQ during conversation with me, but living next to Twain's library in Berkeley must have rubbed something off onto me. |
Background of Twain's Western Adventre and Subsequent Book
The first chapter describes the scene in 1861 when the 26 year old Sammuel Clemens headed West out of the United States on the historic Overland Stage Coach to Carson City, Nevada. Clemens departed from the Western Frontier of the United States crossing the Missouri River at St. Joseph. Twain was traveling by stagecoach outside of the US across the unsettled frontier with his brother, who had been appointed territorial secretary of the Nevada Territory.
Twain's description of this stagecoach voyage alone is a book in itself. In fact, Roughing It is a number of different books all within this single book, with the themes of each story drawn loosely together by no more than having happened in the Wild West during Twain's time wandering the West Coast. That's good enough for me! Roughing It is a travel log, and if nothing else, a view of the wide variety of cultural experiences and physical descriptions of California during the 1860s.
Chapter II through XXI concern Twain's view of America wildly growing through the window of a rapidly moving stagecoach. Mormons, desprados, dust, emigrants, indians and the terrain pour out of these old pages. It starts at the end of "civilization" in 1861, St. Joseph Missouri.
"The first thing we did on that glad evening that landed us at St. Joseph was to hunt up the stage-office, and pay a hundred and fifty dollars apiece for tickets per overland coach to Carson City, Nevada."
The adventure continues after the Stage Ride. Twain's position as Secretary to the Territorial Secretary was not sutiable to employ the time or talents of the young Clemmens to anyone's satisfaction, especially Twain's. So the Young Twain departed to Lake Tahoe to make his fortune in the Wild West as a "Timber Baron."
The territorial government was located in Carson City just a few miles East over the Carson Range from Lake Tahoe in its deeply forested basin.
Despite his failure as a "Timber Baron," Twain left us a remarkable description of the natural beauties of Tahoe Basin before he tried to destroy them with a careless fire, and the subsequent wholesale development altered its face.
Follwoing Twain through an insightful and enlightening series of career faliures rewards the present-day reader with descriptions of Twain's wanderings all about the West, until he finally came to rest as a reporter in the biggest Silver Boom Town of all, Virginia City. From this position Twain is able to give us a good view of the lay of the land, the characters who inhabit it, and the spirit of the times.
Twain was able to get as far as Hawaii during his wanderings. Not a bad place to be while the rest of the nation was tearing itself apart in Civil War.
From Carson City to San Francisco to the remote silver fields along the Eastern flank of the Sierra Nevada to the beaches of Hawaii, Twain gives us remarkable views of the West Coast during the 1860s.
Roughing It's allure perserveres because it is told beyond the terms of it's own day, still revealing to today's readers amazing insights into the physical and social terrains Clemmens experienced. Clemmens gives us looks into the minds of his subjects and the spirit of the times. Clemmens view of both easily crosses the divide of centuries.
Clemmen's approach appears to honestly define both the shared social assumptions & motivations of the pure and open greed that tied Silver Boom culture together, as well as revealing the hard lives of simple people who were driven by the hollow promises of the Silver Boom., as they were by the Gold Rush before.
Deciding that the position of secratary to The Secratary was unsuitable work for the young Clemmens, he and a new young friend who also "got it," as Clemmens puts it, together shouldered axes, gear, and food and started on foot for Lake Tahoe from Carson City. Climbing over the Carson Range into the Tahoe Basin from the Carson Valley, these intrepred spirits intended to carve out lives for themselves as "Timber Barons" out of the dense forests surrounding Lake Tahoe.
From Carson City young Clemmens and his companion set out for Lake Tahoe, which they "were told the distance was 11 miles."
Clemmens subsequently spent 'two or three weeks" camping along the North Shore of Lake Tahoe during the late Summer of 1861.
As our Trail Guide begins our hike South toward Mount Whitney from the Shores of West Lake Tahoe at Meeks Bay, it enriches our experience to understand the history of the Tahoe Basin, or at least take a look at it though Twain's eyes, looking at it in 1861.
Twain's Route to Lake Tahoe
A review of the map reveals a likely route, if you took the easiest way possible, between Carson City and Lake Tahoe, which measures at near 11 miles, however you measure it.
This puts Clemmens and his pal on the Shore of Lake Tahoe about a mile North of Sand Point on the Northeast side of the Lake. Here a skiff had been stashed by their friends in Carson City.
They headed across the water "a three mile pull" to their North Shore camp from where they first encounterd the lake.
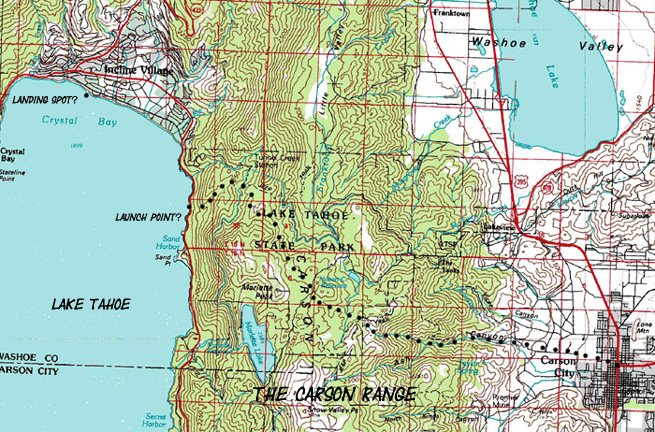
Clemens descriptions and mileages indicate that it is likely that their camp was on the beach near the present location of Incline Village on the North Shore of Lake Tahoe.
The Descriptions
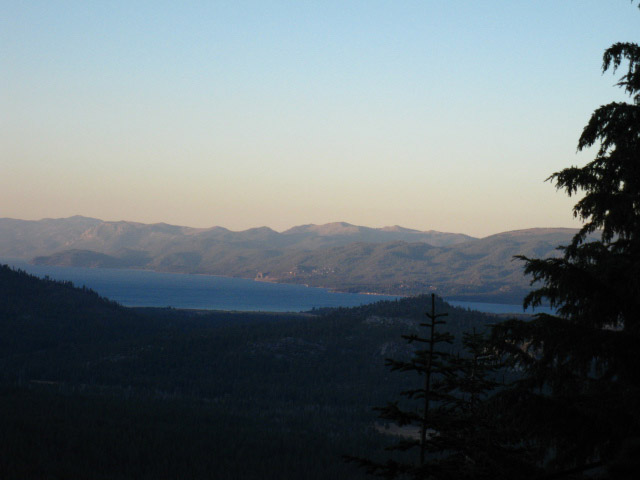

Above: The Carson Range at Sunset across Lake Tahoe.
Lake Tahoe
First View of Lake Tahoe
"...at last the Lake burst upon us—a noble sheet of blue water lifted six thousand three hundred feet above the level of the sea, and walled in by a rim of snow-clad mountain peaks that towered aloft full three thousand feet higher still! It was a vast oval, and one would have to use up eighty or a hundred good miles in traveling around it. As it lay there with the shadows of the mountains brilliantly photographed upon its still surface I thought it must surely be the fairest picture the whole earth affords."
"We were land owners now, duly seized and possessed, and within the protection of the law."
"The forest about us was dense and cool, the sky above us was cloudless and brilliant with sunshine, the broad lake before us was glassy and clear, or rippled and breezy, or black and storm-tossed, according to Nature's mood; and its circling border of mountain domes, clothed with forests, scarred with land-slides, cloven by canons and valleys, and helmeted with glittering snow, fitly framed and finished the noble picture. The view was always fascinating, bewitching, entrancing. The eye was never tired of gazing, night or day, in calm or storm; it suffered but one grief, and that was that it could not look always, but must close sometimes in sleep."
Clemen's "buisness" was..."Ballon Voyages"
"...drifting around in the boat. We were on the north shore. There, the rocks on the bottom are sometimes gray, sometimes white. This gives the marvelous transparency of the water a fuller advantage than it has elsewhere on the lake. We usually pushed out a hundred yards or so from shore, and then lay down on the thwarts, in the sun, and let the boat drift by the hour whither it would. We seldom talked. It interrupted the Sabbath stillness, and marred the dreams the luxurious rest and indolence brought. The shore all along was indented with deep, curved bays and coves, bordered by narrow sand-beaches; and where the sand ended, the steep mountain-sides rose right up aloft into space—rose up like a vast wall a little out of the perpendicular, and thickly wooded with tall pines.
So singularly clear was the water, that where it was only twenty or thirty feet deep the bottom was so perfectly distinct that the boat seemed floating in the air! Yes, where it was even eighty feet deep. Every little pebble was distinct, every speckled trout, every hand's- breadth of sand. Often, as we lay on our faces, a granite boulder, as large as a village church, would start out of the bottom apparently, and seem climbing up rapidly to the surface, till presently it threatened to touch our faces, and we could not resist the impulse to seize an oar and avert the danger. But the boat would float on, and the boulder descend again, and then we could see that when we had been exactly above it, it must still have been twenty or thirty feet below the surface. Down through the transparency of these great depths, the water was not merely transparent, but dazzlingly, brilliantly so. All objects seen through it had a bright, strong vividness, not only of outline, but of every minute detail, which they would not have had when seen simply through the same depth of atmosphere. So empty and airy did all spaces seem below us, and so strong was the sense of floating high aloft in mid-nothingness, that we called these boat-excursions "balloon-voyages."
"While I was at this, I heard a shout from Johnny, and looking up I saw that my fire was galloping all over the premises! Johnny was on the other side of it. He had to run through the flames to get to the lake shore, and then we stood helpless and watched the devastation.
The ground was deeply carpeted with dry pine-needles, and the fire touched them off as if they were gunpowder. It was wonderful to see with what fierce speed the tall sheet of flame traveled! My coffee-pot was gone, and everything with it. In a minute and a half the fire seized upon a dense growth of dry manzanita chapparal six or eight feet high, and then the roaring and popping and crackling was something terrific. We were driven to the boat by the intense heat, and there we remained, spell-bound.
Within half an hour all before us was a tossing, blinding tempest of flame! It went surging up adjacent ridges—surmounted them and disappeared in the canons beyond—burst into view upon higher and farther ridges, presently—shed a grander illumination abroad, and dove again—flamed out again, directly, higher and still higher up the mountain-side- -threw out skirmishing parties of fire here and there, and sent them trailing their crimson spirals away among remote ramparts and ribs and gorges, till as far as the eye could reach the lofty mountain-fronts were webbed as it were with a tangled network of red lava streams. Away across the water the crags and domes were lit with a ruddy glare, and the firmament above was a reflected hell!
Every feature of the spectacle was repeated in the glowing mirror of the lake! Both pictures were sublime, both were beautiful; but that in the lake had a bewildering richness about it that enchanted the eye and held it with the stronger fascination.
We sat absorbed and motionless through four long hours. We never thought of supper, and never felt fatigue. But at eleven o'clock the conflagration had traveled beyond our range of vision, and then darkness stole down upon the landscape again."
"The next morning we started back to the old camp, but while out a long way from shore, so great a storm came up that we dared not try to land. So I baled out the seas we shipped, and Johnny pulled heavily through the billows till we had reached a point three or four miles beyond the camp. The storm was increasing, and it became evident that it was better to take the hazard of beaching the boat than go down in a hundred fathoms of water; so we ran in, with tall white-caps following, and I sat down in the stern-sheets and pointed her head-on to the shore. The instant the bow struck, a wave came over the stern that washed crew and cargo ashore, and saved a deal of trouble. We shivered in the lee of a boulder all the rest of the day, and froze all the night through. In the morning the tempest had gone down, and we paddled down to the camp without any unnecessary delay."
(Alex note: Many years ago, in the late 1960s when I was a boy, my family was camping at South Lake Tahoe. I and another kid who's family was camping nearby, were paddling around in a little yellow life raft; we were crossing the distance between two points, when the wind came up strong, and blew us offshore, over the deep blue of Lake Tahoe. As with Clemens, we paddled for all we were worth for a couple of hours, until the wind abated, and allowed us back to shore. Getting blown into the middle of the lake and freezing at night, or being capsized and drowning, is a real threat to this day.)
"In 1858 silver lodes were discovered in "Carson County," and then the aspect of things changed. Californians began to flock in, and the American element was soon in the majority. Allegiance to Brigham Young and Utah was renounced, and a temporary territorial government for "Washoe" was instituted by the citizens. Governor Roop was the first and only chief magistrate of it. In due course of time Congress passed a bill to organize "Nevada Territory," and President Lincoln sent out Governor Nye to supplant Roop.
At this time the population of the Territory was about twelve or fifteen thousand, and rapidly increasing. Silver mines were being vigorously developed and silver mills erected. Business of all kinds was active and prosperous and growing more so day by day."
This section gives historical depth to our trip through Summit City Creek.
"By and by I was smitten with the silver fever. "Prospecting parties" were leaving for the mountains every day, and discovering and taking possession of rich silver-bearing lodes and ledges of quartz. Plainly this was the road to fortune. The great "Gould and Curry" mine was held at three or four hundred dollars a foot when we arrived; but in two months it had sprung up to eight hundred. The "Ophir" had been worth only a mere trifle, a year gone by, and now it was selling at nearly four thousand dollars a foot! Not a mine could be named that had not experienced an astonishing advance in value within a short time. Everybody was talking about these marvels. Go where you would, you heard nothing else, from morning till far into the night. Tom So-and-So had sold out of the "Amanda Smith" for $40,000—hadn't a cent when he "took up" the ledge six months ago. John Jones had sold half his interest in the "Bald Eagle and Mary Ann" for $65,000, gold coin, and gone to the States for his family. The widow Brewster had "struck it rich" in the "Golden Fleece" and sold ten feet for $18,000—hadn't money enough to buy a crape bonnet when Sing-Sing Tommy killed her husband at Baldy Johnson's wake last spring. The "Last Chance" had found a "clay casing" and knew they were "right on the ledge"—consequence, "feet" that went begging yesterday were worth a brick house apiece to-day, and seedy owners who could not get trusted for a drink at any bar in the country yesterday were roaring drunk on champagne to-day and had hosts of warm personal friends in a town where they had forgotten how to bow or shake hands from long-continued want of practice. Johnny Morgan, a common loafer, had gone to sleep in the gutter and waked up worth a hundred thousand dollars, in consequence of the decision in the "Lady Franklin and Rough and Ready" lawsuit. And so on—day in and day out the talk pelted our ears and the excitement waxed hotter and hotter around us.
I would have been more or less than human if I had not gone mad like the rest. Cart-loads of solid silver bricks, as large as pigs of lead, were arriving from the mills every day, and such sights as that gave substance to the wild talk about me. I succumbed and grew as frenzied as the craziest."
Twain finds hard rock mining difficult
"True knowledge of the nature of silver mining came fast enough...
Therefore, instead of working here on the surface, we must either bore down into the rock with a shaft till we came to where it was rich—say a hundred feet or so—or else we must go down into the valley and bore a long tunnel into the mountain side and tap the ledge far under the earth. To do either was plainly the labor of months; for we could blast and bore only a few feet a day—some five or six. But this was not all. He said that after we got the ore out it must be hauled in wagons to a distant silver-mill, ground up, and the silver extracted by a tedious and costly process. Our fortune seemed a century away!
But we went to work. We decided to sink a shaft. So, for a week we climbed the mountain, laden with picks, drills, gads, crowbars, shovels, cans of blasting powder and coils of fuse and strove with might and main. At first the rock was broken and loose and we dug it up with picks and threw it out with shovels, and the hole progressed very well. But the rock became more compact, presently, and gads and crowbars came into play. But shortly nothing could make an impression but blasting powder.
That was the weariest work! One of us held the iron drill in its place and another would strike with an eight-pound sledge—it was like driving nails on a large scale. In the course of an hour or two the drill would reach a depth of two or three feet, making a hole a couple of inches in diameter. We would put in a charge of powder, insert half a yard of fuse, pour in sand and gravel and ram it down, then light the fuse and run. When the explosion came and the rocks and smoke shot into the air, we would go back and find about a bushel of that hard, rebellious quartz jolted out. Nothing more. One week of this satisfied me. I resigned. Clagget and Oliphant followed. Our shaft was only twelve feet deep. We decided that a tunnel was the thing we wanted.
So we went down the mountain side and worked a week; at the end of which time we had blasted a tunnel about deep enough to hide a hogshead in, and judged that about nine hundred feet more of it would reach the ledge. I resigned again, and the other boys only held out one day longer. We decided that a tunnel was not what we wanted. We wanted a ledge that was already "developed." There were none in the camp.
We dropped the "Monarch" for the time being."
Work in a Silver Stamping Mill
(Check out the Golden Gate Mine gold stamping mill on the Eastern Sierra)
"I had already learned how hard and long and dismal a task it is to burrow down into the bowels of the earth and get out the coveted ore; and now I learned that the burrowing was only half the work; and that to get the silver out of the ore was the dreary and laborious other half of it. We had to turn out at six in the morning and keep at it till dark. This mill was a six-stamp affair, driven by steam. Six tall, upright rods of iron, as large as a man's ankle, and heavily shod with a mass of iron and steel at their lower ends, were framed together like a gate, and these rose and fell, one after the other, in a ponderous dance, in an iron box called a "battery." Each of these rods or stamps weighed six hundred pounds. One of us stood by the battery all day long, breaking up masses of silver-bearing rock with a sledge and shoveling it into the battery. The ceaseless dance of the stamps pulverized the rock to powder, and a stream of water that trickled into the battery turned it to a creamy paste. The minutest particles were driven through a fine wire screen which fitted close around the battery, and were washed into great tubs warmed by super-heated steam—amalgamating pans, they are called. The mass of pulp in the pans was kept constantly stirred up by revolving "mullers." A quantity of quicksilver was kept always in the battery, and this seized some of the liberated gold and silver particles and held on to them; quicksilver was shaken in a fine shower into the pans, also, about every half hour, through a buckskin sack. Quantities of coarse salt and sulphate of copper were added, from time to time to assist the amalgamation by destroying base metals which coated the gold and silver and would not let it unite with the quicksilver.
All these tiresome things we had to attend to constantly. Streams of dirty water flowed always from the pans and were carried off in broad wooden troughs to the ravine. One would not suppose that atoms of gold and silver would float on top of six inches of water, but they did; and in order to catch them, coarse blankets were laid in the troughs, and little obstructing "riffles" charged with quicksilver were placed here and there across the troughs also. These riffles had to be cleaned and the blankets washed out every evening, to get their precious accumulations—and after all this eternity of trouble one third of the silver and gold in a ton of rock would find its way to the end of the troughs in the ravine at last and have to be worked over again some day. There is nothing so aggravating as silver milling. There never was any idle time in that mill. There was always something to do. It is a pity that Adam could not have gone straight out of Eden into a quartz mill, in order to understand the full force of his doom to "earn his bread by the sweat of his brow." Every now and then, during the day, we had to scoop some pulp out of the pans, and tediously "wash" it in a horn spoon—wash it little by little over the edge till at last nothing was left but some little dull globules of quicksilver in the bottom. If they were soft and yielding, the pan needed some salt or some sulphate of copper or some other chemical rubbish to assist digestion; if they were crisp to the touch and would retain a dint, they were freighted with all the silver and gold they could seize and hold, and consequently the pan needed a fresh charge of quicksilver. When there was nothing else to do, one could always "screen tailings." That is to say, he could shovel up the dried sand that had washed down to the ravine through the troughs and dash it against an upright wire screen to free it from pebbles and prepare it for working over.
The process of amalgamation differed in the various mills, and this included changes in style of pans and other machinery, and a great diversity of opinion existed as to the best in use, but none of the methods employed, involved the principle of milling ore without "screening the tailings." Of all recreations in the world, screening tailings on a hot day, with a long-handled shovel, is the most undesirable."
Golden Gate Mine on Mill Road off Hwy 395, Antelope Valley
 |
 |
Above: Golden Gate Mine stamping mill. This mill was served by an ariel tram that brought the gold ore from Golden Gate Peak.
"Mono Lake lies in a lifeless, treeless, hideous desert, eight thousand feet above the level of the sea, and is guarded by mountains two thousand feet higher, whose summits are always clothed in clouds. This solemn, silent, sail-less sea—this lonely tenant of the loneliest spot on earth—is little graced with the picturesque. It is an unpretending expanse of grayish water, about a hundred miles in circumference, with two islands in its centre, mere upheavals of rent and scorched and blistered lava, snowed over with gray banks and drifts of pumice-stone and ashes, the winding sheet of the dead volcano, whose vast crater the lake has seized upon and occupied.
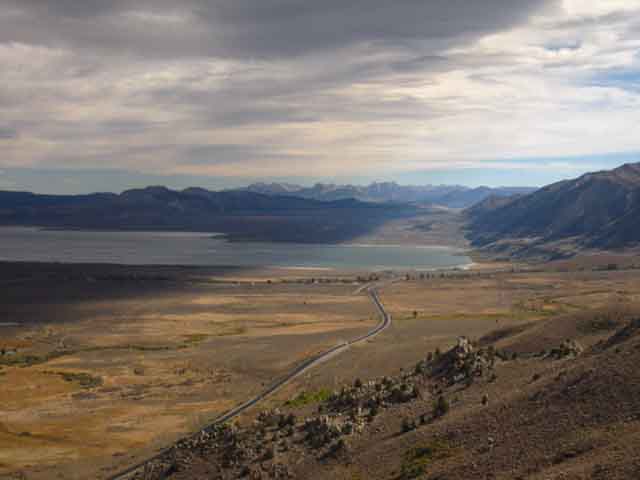 Mono Lake during Fall
Mono Lake during Fall
The lake is two hundred feet deep, and its sluggish waters are so strong with alkali that if you only dip the most hopelessly soiled garment into them once or twice, and wring it out, it will be found as clean as if it had been through the ablest of washerwomen's hands. While we camped there our laundry work was easy. We tied the week's washing astern of our boat, and sailed a quarter of a mile, and the job was complete, all to the wringing out. If we threw the water on our heads and gave them a rub or so, the white lather would pile up three inches high. This water is not good for bruised places and abrasions of the skin. We had a valuable dog. He had raw places on him. He had more raw places on him than sound ones. He was the rawest dog I almost ever saw. He jumped overboard one day to get away from the flies. But it was bad judgment. In his condition, it would have been just as comfortable to jump into the fire.
The alkali water nipped him in all the raw places simultaneously, and he struck out for the shore with considerable interest. He yelped and barked and howled as he went—and by the time he got to the shore there was no bark to him—for he had barked the bark all out of his inside, and the alkali water had cleaned the bark all off his outside, and he probably wished he had never embarked in any such enterprise. He ran round and round in a circle, and pawed the earth and clawed the air, and threw double somersaults, sometimes backward and sometimes forward, in the most extraordinary manner. He was not a demonstrative dog, as a general thing, but rather of a grave and serious turn of mind, and I never saw him take so much interest in anything before. He finally struck out over the mountains, at a gait which we estimated at about two hundred and fifty miles an hour, and he is going yet. This was about nine years ago. We look for what is left of him along here every day."
 Mono Lake under Winter Fog
Mono Lake under Winter Fog
Short fishing trip
to Castle Peak (Hoover Wilderness) "Castle Peak,"-Now Mt. Warren. (see the 13th paragraph)
(There is a small lake below the top of Mt Warren to the East of nearby Oneida Lake.)
"At the end of a week we adjourned to the Sierras on a fishing excursion, and spent several days in camp under snowy Castle Peak, and fished successfully for trout in a bright, miniature lake whose surface was between ten and eleven thousand feet above the level of the sea; cooling ourselves during the hot August noons by sitting on snow banks ten feet deep, under whose sheltering edges fine grass and dainty flowers flourished luxuriously; and at night entertaining ourselves by almost freezing to death. Then we returned to Mono Lake, and finding that the cement excitement was over for the present, packed up and went back to Esmeralda. Mr. Ballou reconnoitred awhile, and not liking the prospect, set out alone for Humboldt."
"There were nabobs in those days—in the "flush times," I mean. Every rich strike in the mines created one or two. I call to mind several of these. They were careless, easy-going fellows, as a general thing, and the community at large was as much benefited by their riches as they were themselves—possibly more, in some cases.
Two cousins, teamsters, did some hauling for a man and had to take a small segregated portion of a silver mine in lieu of $300 cash. They gave an outsider a third to open the mine, and they went on teaming. But not long. Ten months afterward the mine was out of debt and paying each owner $8,000 to $10,000 a month—say $100,000 a year.
One of the earliest nabobs that Nevada was delivered of wore $6,000 worth of diamonds in his bosom, and swore he was unhappy because he could not spend his money as fast as he made it.
Another Nevada nabob boasted an income that often reached $16,000 a month; and he used to love to tell how he had worked in the very mine that yielded it, for five dollars a day, when he first came to the country.
The silver and sage-brush State has knowledge of another of these pets of fortune—lifted from actual poverty to affluence almost in a single night—who was able to offer $100,000 for a position of high official distinction, shortly afterward, and did offer it—but failed to get it, his politics not being as sound as his bank account.
Then there was John Smith. He was a good, honest, kind-hearted soul, born and reared in the lower ranks of life, and miraculously ignorant. He drove a team, and owned a small ranch—a ranch that paid him a comfortable living, for although it yielded but little hay, what little it did yield was worth from $250 to $300 in gold per ton in the market. Presently Smith traded a few acres of the ranch for a small undeveloped silver mine in Gold Hill. He opened the mine and built a little unpretending ten-stamp mill. Eighteen months afterward he retired from the hay business, for his mining income had reached a most comfortable figure. Some people said it was $30,000 a month, and others said it was $60,000. Smith was very rich at any rate.
And then he went to Europe and traveled. And when he came back he was never tired of telling about the fine hogs he had seen in England, and the gorgeous sheep he had seen in Spain, and the fine cattle he had noticed in the vicinity of Rome. He was full of wonders of the old world, and advised everybody to travel. He said a man never imagined what surprising things there were in the world till he had traveled.
One day, on board ship, the passengers made up a pool of $500, which was to be the property of the man who should come nearest to guessing the run of the vessel for the next twenty-four hours. Next day, toward noon, the figures were all in the purser's hands in sealed envelopes. Smith was serene and happy, for he had been bribing the engineer. But another party won the prize! Smith said:
"Here, that won't do! He guessed two miles wider of the mark than I did."
The purser said, "Mr. Smith, you missed it further than any man on board. We traveled two hundred and eight miles yesterday."
"Well, sir," said Smith, "that's just where I've got you, for I guessed two hundred and nine. If you'll look at my figgers again you'll find a 2 and two 0's, which stands for 200, don't it?—and after 'em you'll find a 9 (2009), which stands for two hundred and nine. I reckon I'll take that money, if you please."
The Gould & Curry claim comprised twelve hundred feet, and it all belonged originally to the two men whose names it bears. Mr. Curry owned two thirds of it—and he said that he sold it out for twenty-five hundred dollars in cash, and an old plug horse that ate up his market value in hay and barley in seventeen days by the watch. And he said that Gould sold out for a pair of second-hand government blankets and a bottle of whisky that killed nine men in three hours, and that an unoffending stranger that smelt the cork was disabled for life. Four years afterward the mine thus disposed of was worth in the San Francisco market seven millions six hundred thousand dollars in gold coin.
In the early days a poverty-stricken Mexican who lived in a canyon directly back of Virginia City, had a stream of water as large as a man's wrist trickling from the hill-side on his premises. The Ophir Company segregated a hundred feet of their mine and traded it to him for the stream of water. The hundred feet proved to be the richest part of the entire mine; four years after the swap, its market value (including its mill) was $1,500,000.
An individual who owned twenty feet in the Ophir mine before its great riches were revealed to men, traded it for a horse, and a very sorry looking brute he was, too. A year or so afterward, when Ophir stock went up to $3,000 a foot, this man, who had not a cent, used to say he was the most startling example of magnificence and misery the world had ever seen—because he was able to ride a sixty-thousand-dollar horse—yet could not scrape up cash enough to buy a saddle, and was obliged to borrow one or ride bareback. He said if fortune were to give him another sixty-thousand-dollar horse it would ruin him.
A youth of nineteen, who was a telegraph operator in Virginia on a salary of a hundred dollars a month, and who, when he could not make out German names in the list of San Francisco steamer arrivals, used to ingeniously select and supply substitutes for them out of an old Berlin city directory, made himself rich by watching the mining telegrams that passed through his hands and buying and selling stocks accordingly, through a friend in San Francisco. Once when a private dispatch was sent from Virginia announcing a rich strike in a prominent mine and advising that the matter be kept secret till a large amount of the stock could be secured, he bought forty "feet" of the stock at twenty dollars a foot, and afterward sold half of it at eight hundred dollars a foot and the rest at double that figure. Within three months he was worth $150,000, and had resigned his telegraphic position.
Another telegraph operator who had been discharged by the company for divulging the secrets of the office, agreed with a moneyed man in San Francisco to furnish him the result of a great Virginia mining lawsuit within an hour after its private reception by the parties to it in San Francisco. For this he was to have a large percentage of the profits on purchases and sales made on it by his fellow-conspirator. So he went, disguised as a teamster, to a little wayside telegraph office in the mountains, got acquainted with the operator, and sat in the office day after day, smoking his pipe, complaining that his team was fagged out and unable to travel—and meantime listening to the dispatches as they passed clicking through the machine from Virginia. Finally the private dispatch announcing the result of the lawsuit sped over the wires, and as soon as he heard it he telegraphed his friend in San Francisco:
"Am tired waiting. Shall sell the team and go home."
It was the signal agreed upon. The word "waiting" left out, would have signified that the suit had gone the other way.
The mock teamster's friend picked up a deal of the mining stock, at low figures, before the news became public, and a fortune was the result.
For a long time after one of the great Virginia mines had been incorporated, about fifty feet of the original location were still in the hands of a man who had never signed the incorporation papers. The stock became very valuable, and every effort was made to find this man, but he had disappeared. Once it was heard that he was in New York, and one or two speculators went east but failed to find him. Once the news came that he was in the Bermudas, and straightway a speculator or two hurried east and sailed for Bermuda—but he was not there. Finally he was heard of in Mexico, and a friend of his, a bar-keeper on a salary, scraped together a little money and sought him out, bought his "feet" for a hundred dollars, returned and sold the property for $75,000.
But why go on? The traditions of Silverland are filled with instances like these, and I would never get through enumerating them were I to attempt do it. I only desired to give, the reader an idea of a peculiarity of the "flush times" which I could not present so strikingly in any other way, and which some mention of was necessary to a realizing comprehension of the time and the country.
I was personally acquainted with the majority of the nabobs I have referred to, and so, for old acquaintance sake, I have shifted their occupations and experiences around in such a way as to keep the Pacific public from recognizing these once notorious men. No longer notorious, for the majority of them have drifted back into poverty and obscurity again."
Roughing It, Samuel Clemmens, American Publishing, Hartford Conn., 1872. References for information above Stagecoach ride to Carson City
To Lake Tahoe: 133-134 restorative powers: 135 Timber barons: 136
Life at Tahoe, 1861: 137 Clarity of the Water: 138. Boats floating in air. Clemmens Burns Tahoe Down: 139-140 Dangerous Lake: Storm. 140-141
Carson Valley before and after Silver: 1858, 146-147 Silver Fever: 151, esp quote on 152-
Work in a Silver Stamping Mill: 192-193.
Mono Lake: 201-208
Short fishing trip to Castle Peak (Hoover Wilderness): 207-208 "The Yosemite Book" on Castle Peak: "Castle Peak,"-Now Mt. Warren. (13th paragraph) There is a small lake below the top of Mt Warren to the East of nearby Oneida Lake. |
Last page: Next page:
Sierra History |
I've put together this page on Clemens view of, and participation in, the Silver Boom of the 1860s. I invite you to comment on this page, or add your own insights, resources, and family histories that shine light on the History of the Sierra Nevada Mountain Range. I've got some Muir coming that will blow your mind. The stuff people don't talk about too much. Ha-ha. THIS PAGE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION: STAY TUNED FOR MUCH MORE! COME ON BACK NOW, 'YA HEAR?
Next page: |
Backpacker ForumsHave a general thought about the Sierra Nevada to relate?Post it on
|
| High Sierra Trails | High Sierra Topics |
Anyone can post text comments in the existing forums, but only members can post up new topics, along with images, maps, and formatting.
Trailhead
Contact
Alex Wierbinski

Backpacking Lake Tahoe to Mount Whitney: Your guide to the High Sierra Crest, including the Tahoe to Yosemite, Pacific Crest, and John Muir Trails
